
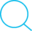
Файлы инициализации shell оболочки - это путь к сохранению единой конфигурации таких параметров, как:
$PATH и других переменных окруженияТо, какие файлы будут загружены и исполнены при зугрузке shell оболочки, зависит от того, какий режим используется, или проще говоря, как эта оболочка была запущена. Существует два основных варианта:
Эти режимы могут быть вручную автивированы при помощи использования следующих ключей:
-l, --login-iВ результате слудующие общие операции будут выполнены:
ssh user@host 'echo $PWD' or with Capistrano: non‑login, non‑interactivessh user@host -t 'echo $PWD': non-login, interactivebash: non‑login, interactivebash myscript.sh: non‑login, non‑interactive#!/usr/bin/env bash shebang: non‑login, non‑interactiveIn order of activation:
/etc/profile~/.bash_profile, ~/.bash_login, ~/.profile (only first one that exists)/etc/bash.bashrc (some Linux; not on Mac OS X)~/.bashrc$BASH_ENV/etc/zshenv~/.zshenv/etc/zprofile~/.zprofile/etc/zshrc~/.zshrc/etc/zlogin~/.zlogin/etc/profile~/.profile$ENV<install-prefix>/config.fish/etc/fish/config.fish~/.config/fish/config.fish.bash_profile or .profile (1st found).profile (Ubuntu, once per desktop login session) + .bashrc.zshenv + .zprofile + .zshrc.profile (Ubuntu, once per desktop login session) + .zshenv + .zshrc.bash_profile or .profile (1st found).zshenv + .zprofile + .zshrcssh or Capistrano: .bashrc.zshenv/usr/libexec/git-core:/usr/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin$PATH/etc/paths, /etc/paths.d/*~/.MacOSX/environment.plist][plist] - affects all graphical programs/etc/launchd.conf/etc/environmentThis guide was tested with:
On these operating systems/apps:
See also:
pam_env(8)
[fish]: http://ridiculousfish.com/shell/user_doc/html/index.html#initialization [plist]: http://developer.apple.com/library/mac/#documentation/MacOSX/Conceptual/BPRuntimeConfig/Articles/EnvironmentVars.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/20002093-113982